- How emotions show up in the body (and why it matters) - February 6, 2026
- How to heal from emotional abuse: A Black woman’s guide to gentle rebuilding - January 29, 2026
- How to process emotions: What it really means and why it’s essential for Black women - January 22, 2026
How does anxiety medication work? It helps balance the chemicals in the brain responsible for stress, fear, and mood regulation—but like any treatment, it comes with side effects and other factors to consider before you decide.

Maybe you’re tired of the chest tightness, racing heartbeat, or worrisome thoughts keeping you up at night—or the way anxiety stops you from focusing on your work, showing up for family and friends, or simply getting through the day.
Or perhaps your doctor already recommended medication, but you’re scared of what that means.
How will it impact my body? Will it change my personality? Will I be on it forever?
These questions are valid, especially if you’re a Black woman who typically avoids medication in general or struggles to see anxiety as a treatable health condition.
But understanding “how does anxiety medication work?” is a great first step.
This guide breaks down just that—what anxiety meds do, how they work, and what to think about as you make whatever choice is best to protect your peace and support your body and overall wellness.
>> MORE: Read this Black woman’s mental health guide (so you can love your mind a little more)
What's in this article?
- 1 How anxiety affects the brain
- 2 How anxiety medications help ease symptoms
- 3 Common types of anxiety medication
- 4 The benefits and drawbacks of anxiety meds—what to know before you decide
- 5 Understanding medication side effects (and what they really mean)
- 6 Should you avoid anxiety medications because of the side effects?
- 7 How to decide if anxiety medication is right for you
- 8 How does anxiety medication work FAQs
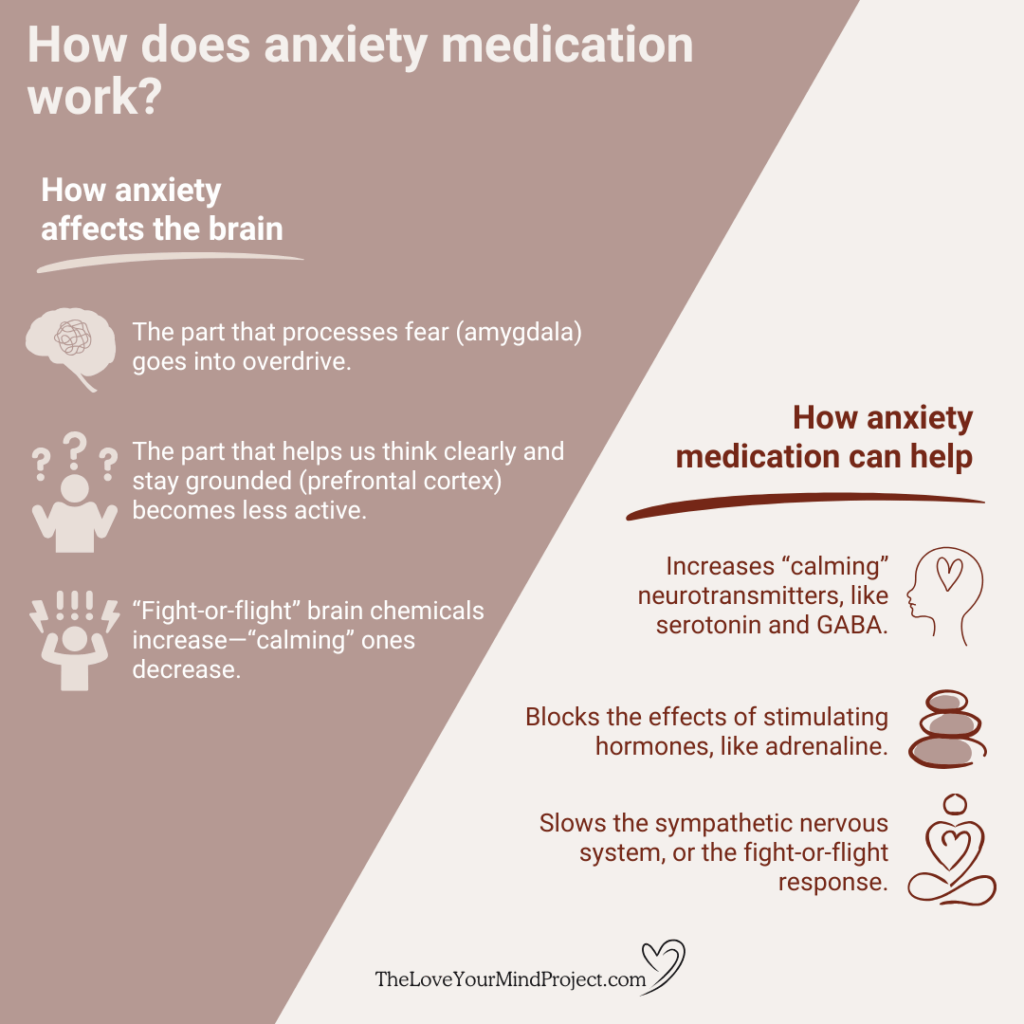
How anxiety affects the brain
Chronic anxiety is more than worrisome thoughts—it’s a legit medical condition that impacts how the brain functions. Here’s how.
When experiencing anxiety1:
- The brain’s stress response becomes overactive: The amygdala—the part of the brain that processes fear—goes into overdrive, signaling danger even when there’s none.
- Thinking clearly gets harder: The prefrontal cortex, which helps us reason, plan, and stay grounded, becomes less active.
- Stress chemicals surge: Brain chemicals that heighten the fight-or-flight response increase. Those responsible for calming or regulating mood decrease.
So while you may think you need to simply stop worrying, have more faith, or pray harder, your brain could be stuck in survival mode—in need of a little help.
>> MORE: Common mental health conditions in women (and how to break the silence)
How anxiety medications help ease symptoms
Anxiety medications mainly work by rebalancing chemicals in the brain. Depending on the type of medication, they might2:
- Increase the amount of “calming” neurotransmitters available in the body, like serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
- Block the effects of stimulating hormones, like adrenaline.
- Slow the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the fight-or-flight response.
Medication doesn’t “cure” anxiety—neither does it change your personality—instead, it aims to provide relief for overwhelming symptoms so you can think, feel, and engage in life more clearly.
“Some of the biggest benefits of taking anxiety medication include improving symptoms, like an increased heart rate, sweaty palms, shaky hands, or feeling like your stomach is in knots,” said Dr. Reba Peoples, psychiatrist and founder of Imara Health and Wellness. “It can also reduce ruminating thoughts and worry—and help you brave social or overstimulating situations with less dread.”
Common types of anxiety medication
There are several categories of anti-anxiety medication, and each one works differently.
Antidepressants: Typically the first choice
Many doctors start with antidepressants when treating severe anxiety. They’re approved for long-term use and primarily work by balancing the production of key brain chemicals3:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Boost serotonin levels, which are linked to positive feelings, to help improve mood. It can take weeks to notice its benefits.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): Increase the availability of serotonin and norepinephrine, which can influence alertness and energy. SNRIs can also help relieve chronic pain.
Benzodiazepines: Fast-acting, but can be habit-forming
Benzodiazepines enhance the effects of GABA, the chemical responsible for slowing nerve activity and calming the body. They can provide quick relief for severe anxiety symptoms or panic attacks. But because the body can build a tolerance, benzodiazepines are typically prescribed for short-term use.4
>> MORE: Try these daily mental health habits for the hard seasons
Beta-blockers: Target physical symptoms
Beta-blockers slow your heart rate and relax your blood vessels by blocking the stimulating effects of adrenaline and norepinephrine. This can help reduce trembling, heart pounding, and other physical symptoms of anxiety. Although mainly used to treat heart conditions, they might be prescribed for situational anxiety, like public speaking.5
The benefits and drawbacks of anxiety meds—what to know before you decide
Exploring medication for anxiety is a personal decision. Weighing the benefits and risks can help you decide what best aligns with your needs and values.
Why you might consider medication as part of your healing journey
Anti-anxiety medication can significantly improve severe symptoms. So if you find it difficult to work, parent, maintain relationships, or even leave the house, medication can settle your nervous system, helping you rest better, gain clarity and focus, and experience less overwhelm.
You might see the most progress when you combine medication with therapy—where you can engage in deeper healing work.
In therapy, you can get to the root of anxiety, understand triggers and unhealthy thought patterns, and build tools to manage and thrive without being overcome by ruminating thoughts, worries, or panic.
>> MORE: Here’s how therapy can help Black women heal
What to watch out for
Every treatment comes with considerations. These aren’t necessarily reasons to avoid anxiety medication, but topics to discuss with your doctor.
- It can take time to find the right medication. Finding the right type and dosage might take several rounds of prescribing, waiting, and sharing what’s working and what’s not with your provider.
- Certain medications can be habit-forming—specifically, benzodiazepines. If your doctor prescribes them, ask about the plan for monitoring and tapering off.
- Some meds interact poorly with others. Share your medications, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements with your provider so they can keep you safe.
- If it’s more than anxiety, anxiety meds may not be enough: Anxiety medications can help with mood disorders, like bipolar disorder, but they usually require close monitoring and may also include stabilizers to minimize extreme mood swings.6
Understanding medication side effects (and what they really mean)
Side effects can sound scary, but understanding them can help you make an informed decision about what’s best for you.
What are side effects?
Side effects are possible reactions people may have when taking a medication. They’re identified during clinical trials and can include any unwanted or unintended effect, from a runny nose to a life-threatening condition, even death.
All drugs have potential side effects.7 But not everyone will experience them.
Drug companies typically list the most common ones, but even those are based on who’s represented in the clinical studies—normally white participants.
Black women tend to be underrepresented in clinical trials8, but that doesn’t mean the medication won’t work for us or that we should avoid it. However, it does highlight the importance of finding a culturally competent healthcare provider who will listen to our unique symptoms and experiences with a given medication.
>> MORE: How to choose self-love over mental health stigma
Common side effects of anxiety medications
The most common side effects are mild and often fade with time. Here are a few examples from commonly prescribed medications.9,10
- SSRIs and SNRIs (Lexapro, Zoloft): Dizziness, headaches, dry mouth, sleep changes, or decreased libido (low sex drive).
- Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Ativan): Drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, and higher dependency risk.4
- Beta blockers, like propranolol: Fatigue, dry mouth or eyes, and dizziness (especially upon standing).5
Of course, some side effects can be severe, especially for people with certain chronic health conditions. So don’t overlook them.
“There are certainly side effects that can come with anxiety medication,” said Dr. Peoples. “It’s important to discuss your lifestyle and the potential risks and benefits of each type with your doctor so they can prescribe the one that’s best for you.”
>> MORE: How to find a therapist for the first time (and what to expect)
Should you avoid anxiety medications because of the side effects?
The short answer? You should consider a treatment when its benefits outweigh the risks. This is typically how doctors approach prescribing.
But your lifestyle, preferences, and comfort level matter.
So, you can avoid anxiety medication if you don’t like the idea. You can also try it and see how your body responds. If you don’t like how you feel when taking it, you can discuss adjusting the dose, swapping the meds, or stopping it altogether.
The bottom line is that this is your decision and no one else’s—but it’s one best made with a provider who sees, hears, and understands your lived experience.
“Ultimately, we want you to feel like yourself with medication,” said Dr. Peoples. “So if you notice you feel slowed down, emotionally numb, or that something is just ‘off,’ let your doctor know so they can make adjustments if needed.”
>> MORE: Learn more about anxiety
How to decide if anxiety medication is right for you
When deciding if you should try anxiety medication, start with what you’re feeling.
“Evaluate the impact anxiety has on your quality of life or ability to function,” said Dr. Peoples. “If you feel significantly limited in those areas, medication may help improve your overall well-being considerably.”
Talk openly with your doctor or therapist. Be honest about any fears or reservations regarding your treatment options. Together, you can figure out the best way for you to find relief from anxiety—whether that includes medication or not.
>> SUBSCRIBE for weekly resources, tools, and encouragement in your inbox
How does anxiety medication work FAQs
Do anxiety medications really work?
Yes, anxiety medication can help relieve debilitating symptoms, like trembling, trouble focusing, racing thoughts, and rapid heartbeat. Medications don’t cure anxiety, but they can improve your quality of life.
How does anxiety medication make you feel?
The goal of anxiety medication is to help you feel relief—calmer, more focused, less reactive, and more grounded. But individuals’ experiences will vary. It’s important to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and treatment options with your doctor.
Do anxiety meds help with overthinking?
Anti-anxiety medications can help with overthinking. By regulating the brain chemicals associated with fear and hyperarousal, they can reduce the intensity and frequency of racing and worrying thoughts. But consider pairing medication with therapy to get to the root causes of anxiety.
What is the most common anxiety medication?
Antidepressants are the most commonly prescribed type of anxiety medication. SSRIs, like sertraline (Zoloft) and escitalopram (Lexapro), help balance the chemicals in the brain that regulate calming and stimulating effects.
What anxiety medication has the fewest side effects?
Doctors generally start with an SSRI because it has a long history of being effective and has fewer side effects compared to older anxiety medications. But everyone responds differently. Side effects can vary depending on the type of medication, a person’s medical history, lifestyle, and other factors.
What is the biggest problem with anti-anxiety drugs?
Finding the right medication and dosage can take time. And drugs, like benzodiazepines, can be habit-forming. Always discuss the benefits and potential risks with your doctor before starting a medication. Open communication with your healthcare provider can make this process easier and safer.
How do I find the best anxiety medication for me?
Talk with your primary care provider, psychiatrist, or nurse practitioner to find the best starting point based on your symptoms. They should consider your medical history, lifestyle, and preferences—and be willing to check in regularly—because that’s what you deserve.
References
Last accessed November 2025
- Martin, E. I., Ressler, K. J., Binder, E., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2009). The Neurobiology of Anxiety Disorders: Brain Imaging, Genetics, and Psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 32(3), 549–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2009.05.004 ↩︎
- Clinic, C. (2023, March 2). Anxiolytics are medications that treat anxiety and related conditions. Many drugs have this effect, and anxiolytics are among the most prescribed drugs worldwide. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24776-anxiolytics ↩︎
- Clinic, C. (2023, September 5). Antidepressants treat conditions like depression, anxiety and more. They help with symptoms but often work best with therapy. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/9301-antidepressants-depression-medication ↩︎
- and, Ssri. (2020, May 26). SSRIs and Benzodiazepines for General Anxiety Disorders (GAD). Adaa.org. https://adaa.org/learn-from-us/from-the-experts/blog-posts/consumer/ssris-and-benzodiazepines-general-anxiety ↩︎
- Clinic, C. (2022, February 2). Beta-blockers treat a wide range of cardiovascular conditions, like high blood pressure. They slow down your heart rate and relax your blood vessels. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22318-beta-blockers ↩︎
- Bipolar disorder – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2025). Mayoclinic.org; https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bipolar-disorder/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355961 ↩︎
- Shmerling, R. H. (2024, November 20). Medication side effects: What are your options? – Harvard Health. Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/medication-side-effects-what-are-your-options-202411203082 ↩︎
- Le, D., Ozbeki, H., Salazar, S., Berl, M., Turner, M. M., & Price, O. A. (2022). Improving African American women’s engagement in clinical research: A systematic review of barriers to participation in clinical trials. Journal of the National Medical Association, 114(3), 324–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnma.2022.02.004 ↩︎
- Clinic, C. (2023, September). SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are a class of antidepressants. They help treat depression and anxiety, among other conditions. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24795-ssri ↩︎
- Clinic, C. (2023, September). SNRIs are antidepressants that ease depression, anxiety and chronic pain. They work by balancing brain chemicals. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24797-snri ↩︎